Verbs – வினைச்சொல்
வினையை அல்லது செயலை குறிக்கும் சொல் வினைச்சொல் ஆகும். Verb என்பது ஒரு செயல், நிகழ்ச்சி அல்லது நிலையை காட்டும் வார்த்தை.
Verbs are words that show an action, event, or state. English sentences are usually not complete without a verb.
எடுத்துக்காட்டாக:
Do – செய்
Come – வா
Speak – பேசு
Go – போ
Ranjith went to school.
ரஞ்சித் பள்ளிக்குச் சென்றான்.
Abi dances very well.
அபி மிக நன்றாக நடனமாடுகிறாள்.
Anitha is a teacher.
அனிதா ஒரு ஆசிரியராக இருக்கிறார்.
Mohan will come to my house
மோகன் என்னுடைய வீட்டுக்கு வருவான்.
He has sung a song.
அவன் ஒரு பாட்டுப் பாடியிருக்கிறான்.
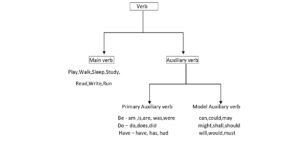
Types of Verbs (Verb வகைகள்)
1. Main Verbs (முக்கிய வினைச்சொல்)
Main Verbs (also called Lexical Verbs) are the words that express the main action, event, or state of being in a sentence. These show the main action in a sentence.
Main Verbs – “ஒரு வாக்கியத்தில் முக்கியமான செயல் அல்லது நிலையைச் சொல்வது. இவை வாக்கியத்தின் மையப் பொருளை தரும் சொற்கள்.” இவை வாக்கியத்தில் முக்கியமான செயலைக் குறிக்கும்.
Examples:
-
run (ஓடு), eat (சாப்பிடு), play (விளையாடு), write (எழுது)
-
I play cricket. – ‘play’ is the main verb.
நான் கிரிக்கெட் விளையாடுகிறேன். -
She sings well. – ‘sings’ is the main verb.
அவள் நன்றாகப் பாடுகிறாள்.
Types of Main Verbs
Main verbs can show:
-
Action – செயலை
-
State – நிலையை
-
Feeling – உணர்ச்சியை
Action Verbs (செயல் வினைகள்)
These verbs show an action you can see someone doing.
Examples:
run (ஓடுதல்) – I run fast. (நான் வேகமாக ஓடுகிறேன்.)
write (எழுதல்) – He writes a letter. (அவன் கடிதம் எழுதுகிறான்.)
eat (சாப்பிடுதல்) – We eat rice. (நாங்கள் சாதம் சாப்பிடுகிறோம்.)
Stative Verbs (நிலை வினைகள்)
These verbs show a state, condition, possession, or mental status, not an action.
Examples:
-
be (இரு) – She is happy. (அவள் மகிழ்ச்சியாக இருக்கிறாள்.)
-
have (கொள்) – I have a car. (எனக்கு ஒரு கார் இருக்கிறது.)
-
know (தெரி) – They know the answer. (அவர்களுக்கு விடை தெரியும்.)
Main Verbs
(முக்கிய வினைச்சொல்)
| Verb | Tamil Meaning | Example in Spoken English | Tamil Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| go | போ | I go to school every day. | நான் தினமும் பள்ளிக்கு செல்கிறேன். |
| come | வா | Please come here. | தயவு செய்து இங்கு வா. |
| eat | சாப்பிடு | We eat dinner at 8 pm. | நாங்கள் இரவு உணவை 8 மணிக்கு சாப்பிடுகிறோம். |
| drink | குடி | He drinks coffee daily. | அவன் தினமும் காபி குடிக்கிறான். |
| run | ஓடு | They run in the park. | அவர்கள் பூங்காவில் ஓடுகிறார்கள். |
| read | படி | I read the newspaper in the morning. | நான் காலை செய்தித்தாள் படிக்கிறேன். |
| write | எழுது | She writes short stories. | அவள் சிறுகதைகள் எழுதுகிறாள். |
| sleep | தூங்கு | Babies sleep a lot. | குழந்தைகள் அதிகம் தூங்குகிறார்கள். |
| speak | பேசு | We speak Tamil at home. | நாங்கள் வீட்டில் தமிழ் பேசுகிறோம். |
| watch | பார் (படம்/டிவி) | They watch movies every weekend. | அவர்கள் ஒவ்வொரு வார இறுதியிலும் படங்களை பார்க்கிறார்கள். |
2. Auxiliary Verbs (Helping Verbs) உதவிக்கள்
auxiliary verbs (also called helping verbs) are verbs used together with a main verb to add meaning about time, mood, voice, or to form questions and negatives. These help the main verb and give more details about time, mood, or voice.
செயல்துணை வினைகள் — முதன்மை வினைக்கு துணையாக வந்து, அந்த வாக்கியத்தின் காலம், விதம், கேள்வி, மறுப்பு போன்றவற்றை வெளிப்படுத்தும் சொற்கள். இவை முக்கிய verb-க்கு உதவுகிறது மற்றும் tense/mood பற்றி கூறும்.
Common Auxiliary Verbs:
-
be (am, is, are, was, were) – இருக்க
-
have (has, have, had) – வைத்திருக்க
-
do (do, does, did) – செய், செய்து
Examples:
-
I am eating. – நான் சாப்பிட்டு இருக்கிறேன்.
-
She has finished. – அவள் முடித்துவிட்டாள்.
-
I am going to school. – நான் பள்ளிக்கு போகிறேன்.
Types of Auxiliary Verbs (Auxiliaries-இன் வகைகள்)
Auxiliary verbs are generally divided into two main types:
1.Primary Auxiliaries (முதன்மை துணை வினைகள்)
-
-
be (am, is, are, was, were, been, being)
-
have (have, has, had)
-
do (do, does, did)
-
A. BE verbs (am, is, are, was, were, been, being)
Usage:
-
Continuous Tenses (நடைபெற்று கொண்டிருக்கும் காலம்) – “am/is/are” + verb-ing
She is sleeping. – அவள் தூங்கிக் கொண்டிருக்கிறாள்.
-
Passive Voice (வேற்றுமை வினை)
The book was written by him. – அந்த புத்தகம் அவரால் எழுதப்பட்டது.
-
Linking verb (பொருள் மற்றும் பெயரை இணைக்க)
He is a doctor. – அவர் ஒரு மருத்துவர்.
B. HAVE verbs (have, has, had)
Usage:
-
Perfect Tenses (முடிந்த காலங்கள்)
I have finished my homework. – நான் வீட்டுப்பாடத்தை முடித்துவிட்டேன்.
-
Possession (கைப்பற்றல்)
She has a car. – அவளிடம் ஒரு கார் உள்ளது.
C. DO verbs (do, does, did)
Usage:
-
Questions (கேள்விகள்)
Do you like tea? – உங்களுக்கு தேநீர் பிடிக்குமா?
-
Negatives (மறுப்பு)
I do not know him. – நான் அவரை அறியவில்லை.
Emphasis (வலியுறுத்தல்)
I do understand your problem. – உங்கள் பிரச்சனை எனக்கு உணரப்படுகிறது.
2.Modal Auxiliaries (முறைக் குறிப்புச் செயல்துணை வினைகள்)
-
-
can, could, may, might, will, would, shall, should, must, ought to, need, dare, used to
-
A. CAN / COULD
-
can – present/future ability, possibility
-
could – past ability, polite requests
Examples:
-
I can swim. → நான் நீந்த தெரியும். (திறன்)
-
Could you help me? → நீங்கள் எனக்கு உதவ முடியுமா? (மென்மையான கோரிக்கை)
B. MAY / MIGHT
-
Express permission or possibility
Examples:
-
You may leave now. → நீங்கள் இப்போது செல்லலாம். (அனுமதி)
-
It might rain today. → இன்று மழை பெய்யக்கூடும். (சாத்தியம்)
C. WILL / WOULD
-
will – future tense, strong intention
-
would – polite requests, hypothetical situations
Examples:
-
I will visit Chennai tomorrow. → நான் நாளை சென்னை செல்கிறேன்.
-
Would you like some tea? → உங்களுக்கு சிறிது தேநீர் வேண்டுமா?
D. SHALL / SHOULD
-
shall – future (less common in spoken American English), obligation
-
should – advice or duty
Examples:
-
We shall overcome. → நாங்கள் வெல்லுவோம்.
-
You should eat healthy food. → நீங்கள் ஆரோக்கியமான உணவை சாப்பிட வேண்டும்.
E. MUST
-
Strong necessity or obligation
Example:
-
You must wear a helmet. → நீங்கள் ஹெல்மெட் அணிய வேண்டும்.
F. OUGHT TO
-
Moral duty, recommendation
Example:
-
You ought to respect elders. → நீங்கள் மூத்தோரை மதிக்க வேண்டும்.
G. NEED / DARE
-
Need (necessity), Dare (courage, mostly negative/interrogative)
Examples:
-
You need not worry. → நீங்கள் கவலைப்பட வேண்டாம்.
-
Dare he question me? → அவன் எனக்கே கேள்வி கேட்க்க துணிகிறானா?
3. Modal Verbs (திரை மாற்று verbs)
Modal verbs are special helping verbs in English that show ability, possibility, necessity, permission, advice, obligation, or probability.
They are always followed by the base form of the main verb (without “to”). Modals show ability, possibility, permission, or necessity.
For example: can go, must study, should call.
மோடல் வேர்ப்ஸ் என்பது ஆங்கிலத்தில் உதவி வினைச்சொற்கள்.
இவை ஒரு செயலை செய்வதற்கான திறன், சாத்தியம், அனுமதி, கடமை, அறிவுரை போன்றவற்றைக் காட்டப் பயன்படுகிறது. முக்கியமா, இவை பிறகு வரும் வினைச்சொல் base form-இல் இருக்கும்.இவை ஒரு வேலை செய்ய எண்ணம், அனுமதி, தேவையை குறிக்கும்.
Common Modals:
-
can (முடியும்)
-
could (முடிந்தது/முடியும்)
-
will (செய்வேன்)
-
would (செய்வேன்/செய்வது)
-
shall/should (செய்ய வேண்டும்)
-
may (இருக்கலாம்/அனுமதி)
-
might (இருக்க வாய்ப்பு)
-
must (வேண்டும்)
Examples:
-
I can swim. – நான் நீந்த முடியும்.
-
You must study. – நீ படிக்கவேண்டும்.
1.CAN
Uses:
-
Ability – I can swim. (எனக்கு நீந்தத் தெரியும்.)
-
Permission – You can sit here. (நீங்கள் இங்கே உட்காரலாம்.)
-
Possibility – It can be dangerous. (இது ஆபத்தானதாக இருக்கலாம்.)
Spoken Tip: “Can” is very common in real conversation for abilities or informal permission.
2. COULD
Uses:
-
Past ability – I could run fast when I was young. (நான் இளமையில் வேகமாக ஓட முடிந்தது.)
-
Polite request – Could you help me? (நீங்கள் எனக்கு உதவ முடியுமா?)
-
Possibility – It could rain later. (பின்னர் மழை பெய்யக்கூடும்.)
Spoken Tip: “Could” is softer, politer than “Can” in requests.
3. MAY
Uses:
-
Permission (formal) – You may leave now. (நீங்கள் இப்போது போகலாம்.)
-
Possibility – She may be at home. (அவள் வீட்டில் இருக்கலாம்.)
Spoken Tip: “May” is more formal than “Can,” used in polite or official situations.
4. MIGHT
Uses:
-
Weak possibility – It might snow tonight. (இரவு பனி பெய்யக்கூடும்.)
-
Suggestion (less common) → You might try restarting the computer. (கம்ப்யூட்டரை ரீஸ்டார்ட் செய்து பார்க்கலாம்.)
Spoken Tip: “Might” is used when the possibility is unsure, weaker than “May”.
5. MUST
Uses:
-
Strong necessity / obligation – You must wear a helmet. (நீங்க ஹெல்மெட் கட்டாயம் அணிய வேண்டும்.)
-
Logical conclusion -He must be tired. (அவர் சோர்வாக இருக்கிறார் என்பதில் சந்தேகம் இல்லை.)
Spoken Tip: In strong spoken English, “must” adds authority.
6. SHALL
Uses:
-
Offer/suggestion (British style) – Shall we dance? (நாம் ஆடலாமா?)
-
Future tense (formal) – I shall return. (நான் திரும்பி வருவேன்.)
Note: In modern spoken English (especially American), “shall” is rare except in formal or legal contexts.
7. SHOULD
Uses:
-
Advice – You should eat more fruits. (நீங்கள் அதிகமாக பழங்கள் சாப்பிட வேண்டும்.)
-
Expectation – The train should arrive soon. (பள்ளி விரைவில் வரும்.)
Spoken Tip: “Should” makes advice softer and polite.
8. WILL
Uses:
-
Future – I will call you tomorrow. (நான் நாளை உங்களை அழைப்பேன்.)
-
Willingness – I will help you. (நான் உங்களுக்கு உதவுவேன்.)
Spoken Tip: “Will” is the most common modal for future intention.
9. WOULD
Uses:
-
Polite request – Would you pass me the salt? (சிறிது உப்பு கொடுத்துவிடுவீர்களா?)
-
Past habit – When we were kids, we would play in the fields. (நாங்கள் சிறுவர்களாக இருந்தபோது வயல்களில் விளையாடுவோம்.)
-
Hypothetical – I would travel if I had the money. (பணம் இருந்தால் நான் பயணம் செய்வேன்.)
Spoken Tip: “Would” is powerful for polite, hypothetical speech.
10. OUGHT TO
Uses:
-
Moral duty/Advice – You ought to respect your elders. (நீங்கள் பெரியவர்களை மதிக்க வேண்டும்.)
Verb Forms (Verb-ன் வடிவங்கள்)
English verbs usually have different forms based on tense.
1. Base Form (Root):
-
go (போ)
-
speak (பேசு)
2. Past Simple:
-
went (போனேன்)
-
spoke (பேசியேன்)
3. Past Participle:
-
gone (போய்விட்டேன்)
-
spoken (பேசியிருக்கிறேன்)
Examples:
-
I go to school. – நான் பள்ளிக்கூடம் போகிறேன்.
-
I went to school. – நான் பள்ளிக்கூடம் போனேன்.
-
I have gone to school. – நான் பள்ளிக்கூடம் போய்விட்டேன்.